Concept-Cognitive Learning Survey: Mining and Fusing Knowledge From Data
Motivation
- People learning new concepts can often generalize successfully from just a single example, while machine learning algorithms typically require much more examples to perform with similar accuracy.
- The research of AI should focus on the learning of human-level conceptual knowledge.
Definitions
concept: the common essential characteristics of things abstracted and summarized by human beings in the process of understanding the world.
standard concept := annotation (concept name) + connotation (concept definition) + denotation (referent of concept)
formal context:
, where : a finite set of objects : a finite set of attributes : a binary relation (“incidence”) between objects and attributes - Each element
indicates whether an object possesses an attribute .

- A formal context can be represented by a matrix where each row corresponds to an object, each column corresponds to an attribute, and each value corresponds to the incidence of the object and the attribute.
- The acquisition of formal context is relevant to the following data processing techniques:
- normalization
- discretization
- regularization
- fuzzification
formal concept:
Givenand . Let
denote the set of all attributes shared by the objects in . Let
denote the set of all objects sharing the attributes in . is a formal concept iff the set of attributes shared by the objects in is identical to , and dually, the set of all objects sharing the attributes in is identical to , i.e. and . is the extent of . is the intent of .
Concept Representation and Learning
Formal Concept Analysis (FCA)
- FCA is a means of formally describing concepts and constructing concept lattices.
- FCA expresses objects, attributes, and their relations based on a formal context that comprises the ontology in a structured manner.
- FCA enables the construction of all concepts and their generalization and specialization relationships, forming a concept lattice for the clear expression of the knowledge structure. In this way, concepts can be concretely expressed in various forms to describe the semantic interpretation of the ontology in different scenarios.
- Limitation: Concept lattice construction is an NP-hard problem.
Cognitive Concept Learning
Cognitive model based on granular computing (粒度计算)
- sufficient relationship and necessary relationship between objects and attributes
- the unity of objects and attributes forms the concept
two way learning process
Cognitive concept learning should be carried out from three levels
- philosophy level
- algorithm / technique level
- applicaiton level
Two-way concept learning (TCL)
- sufficient and necessary learning
Limitation
Cognitive concept learning is limited by the framework of granular computing.
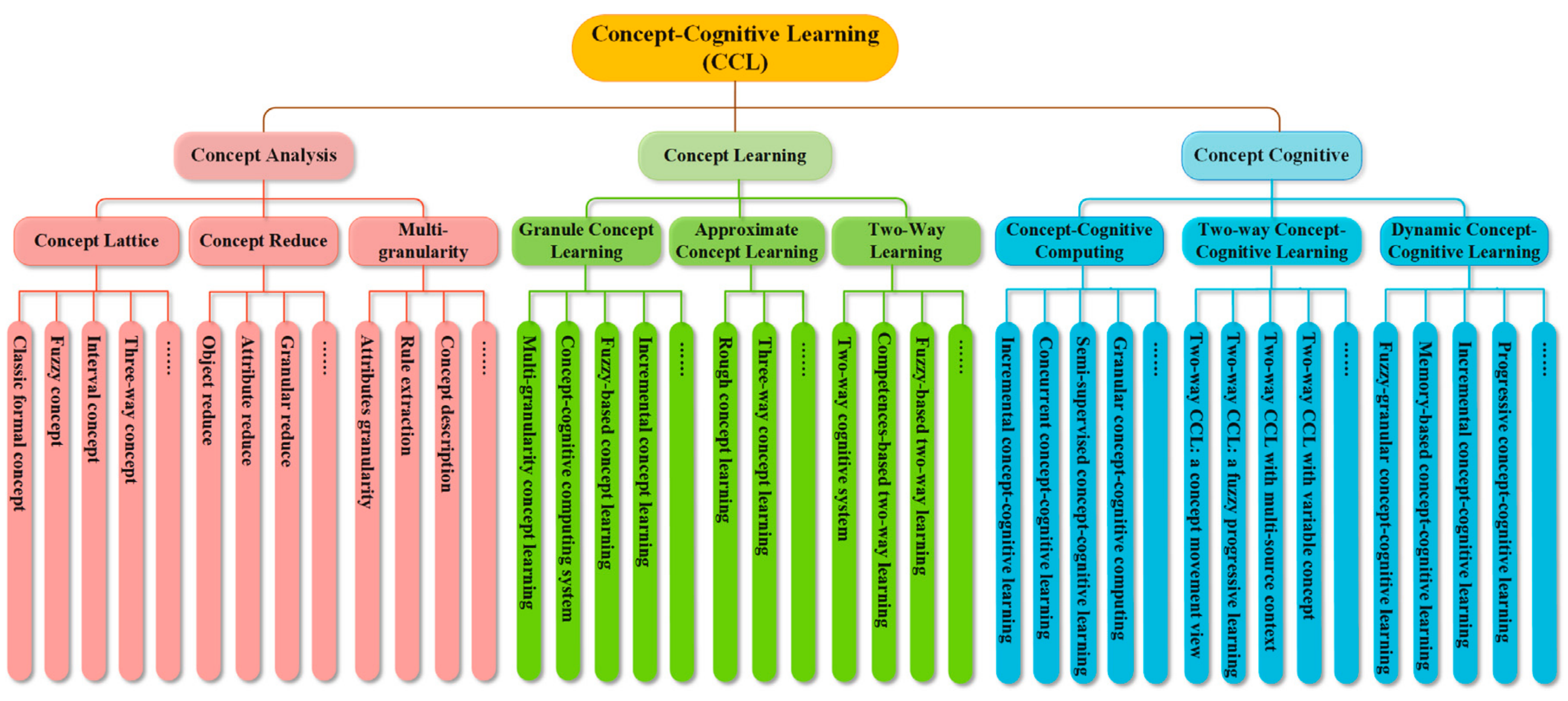
Concept-Cognitive Learning (CCL)
Difference from FCA and Cognitive Concept Learning
- CCL: explore human-level information processing and conceptual knowledge learning mechanisms from a cognitive viewpoint
- FCA: construction of concept lattices
- Cognitive Concept Learning: granular computing
Core concerns of CCL
- concept cognition mechanism
- concept learning method
- cognitive system construction mechanism
- complex decision optimization mechanism
CCL Models
- memory-based CCL model
- incremental CCL model
- fuzzy-based CCL model
- two-way CCL model
- semi-supervised CCL model
RQs
- Why is it important to develop a cognitive learning framework based on concept?
- What is Concept-Cognitive Learning (CCL)?
- How to implement CCL?
Data-Information-Knowledge-Wisdom (DIKW) Hierarchy Model
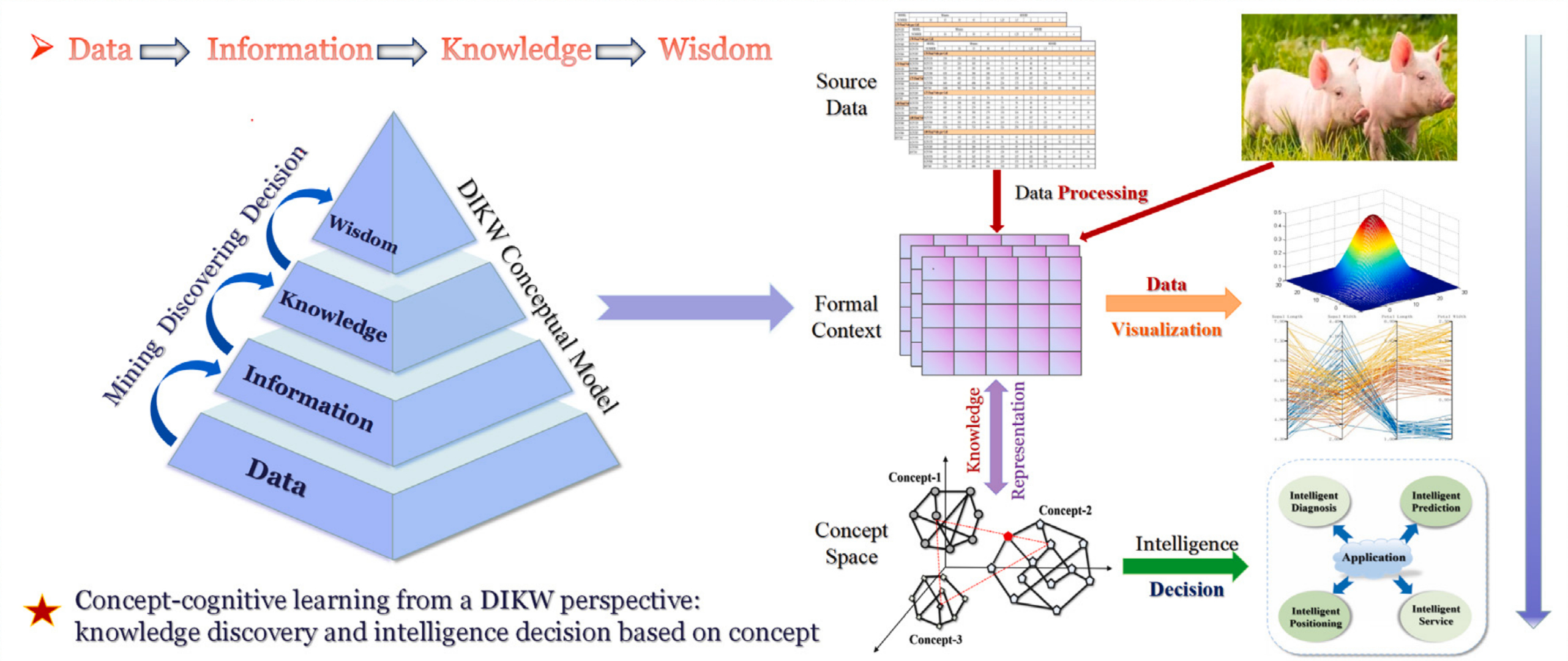
- Data creates information. Information creates knowledge. Knowledge creates wisdom.
- In this process, CCL emphasizes transforming source data into a formal context, representing knowledge as concepts, and applying these concepts within a structured concept space.
- Applications:
- knowledge discovery
- intelligence decision analysis
The Information Processing Triangle
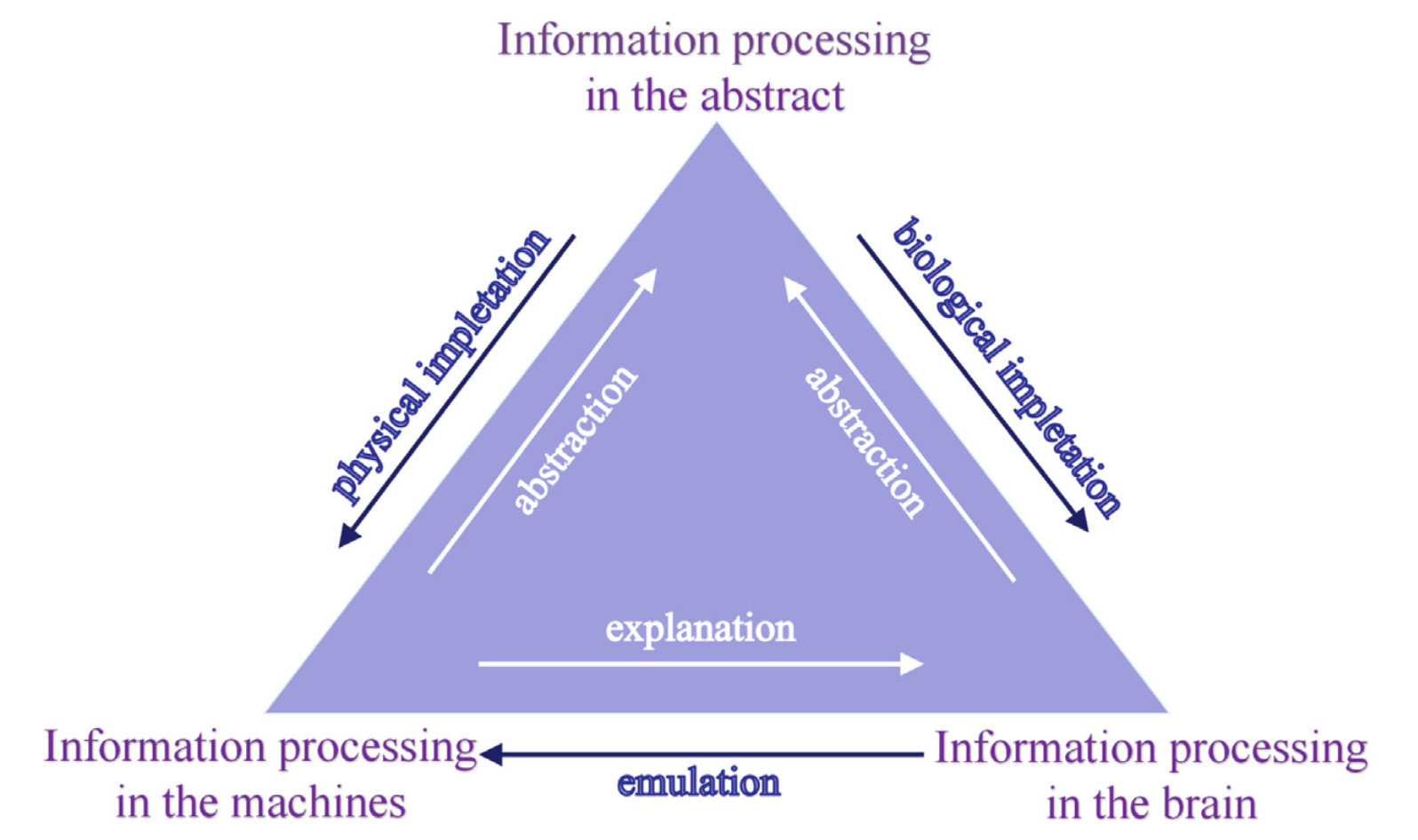
Cognitive concepts may be investigated in three levels
Abstract level: mathematics and logics
- Objective: concept formation learning
- Concept is a knowledge structure existing in the human brain, and also a cognitive process.
- Concepts are formed by abstracting the perceived essential characteristics of things, and by generalizing or inducting in the cognition process.
(概念是在认知过程中对事物的本质特征进行抽象,并加以概括或归纳形成的。)mathematical characterization of concepts formal concept: represent the knowledge structure of concept ontology within a formal context FCA
- a theory that utilizes order theory and complete lattices for data analysis, information processing, and knowledge management
- methods:
- a concept model based on a dual Galois connection
- logical and cognitive mechanism of brain
- concept algebra
- conceptual knowledge structure
- concept learning triangle, three levels of concept information processing (philosophy, algorithm/technique, application)
- structured description of concepts
- mathematical model
- granule description based on FCA
- attribute granulation in formal context
- concept types
- AFS-concept
- abstract concepts
- concept tree
- multi-adjoint concept
- three-way concept
- two-way concept
Machine level: artificial intelligence
- Objective: model and application of concept learning
- concept: the smallest unit of knowledge
- concept learning:
- discovering and acquiring concepts
- analyzing types and structures of concepts
- analyzing relationships between concepts
- using concepts for downstream applications
Challenge: Learning concepts with strong generalization and clear semantic interpretation.
Methods:
- a two-way concept learning mechanism in fuzzy formal context
- a concept learning model with three cognitive properties
- human-level concept learning
- a semi-supervised CCL method based on concept space
- incremental learning of CCL for classification task
Brain level: cognitive simulation
- Objective: simulating human cognitive processes

- cognitive memory functionalities of bidirectional associative memory
- a three-way conceptual approach for cognitive memory functionalities
- a multi-level cognitive concept learning strategy
- an incremental concept learning method
- CCL using concept tree
- an incremental incomplete CCL model
- a two-way concept learning mechanism from a movement view
- fuzzy progressive learning
- combine human memory mechanism with CCL for fuzzy data analysis and knowledge fusion
Research goals
Concept Analysis Method
- Goals:
- characterize knowledge embedded in data
- analyze concept properties and relations
- explore the applicability of concepts
- Concept Lattice
- classical formal concepts
- boolean data,
0-1 binary relationship between objects and attributes
- boolean data,
- fuzzy concepts
- AFS-concepts
- three-way concepts
- Current research in CCL focuses more on exploring various concepts and concept relationships in lattices, rather than on how to construct concept lattices (This is the objective of FCA).
- classical formal concepts
- Concept Reduction
- Goal: optimize storage space, enhance knowledge discovery
- Core idea: selectively remove certain concepts based on specific conditions
- types:
- object reduction
- attribute reduction
- granular reduction
- Methods:
- partial concept forgetting
- fuzzy-granular CCL via three-way decision for dynamic knowledge discovery based on the big concept priority principle
- multi-granularity analysis:
- object- & attribute granularity, rule extraction, granular description
Concept Learning Strategy
- Goals:
- discover and acquire concepts
- conduct in-depth analyses and applications
- Two-way learning:
- acquisition of additional knowledge (i.e. concepts) from the unknown data via
- sufficient concept learning, and
- necessary granule concept learning
- a cognitive process that learns from useless information
- Methods:
- arbitrary information granule transformation
- two-way concept learning for fuzzy formal context
- interval-based two-way concept learning in interval-valued formal context
- acquisition of additional knowledge (i.e. concepts) from the unknown data via
- Granule concept learning
- object granule concept
- attribute granule concept
- Methods:
- multi-granularity concept learning
- fuzzy-based concept learning using conceptual clustering
- concept cognitive computing for dynamic classification
- Approximate concept learning
- rough concept learning
- three-way concept learning
- Methods:
- learning approximating cognitive concepts using an approximate space of a rough set
- progressive fuzzy three-way concept learning
Concept Cognitive Mechanism
- Goal: mining and fusing knowledge from data
- “concept-cognitive learning”
- two-way concept-cognitive learning
- concept movement,
relationship between various two-way granular concepts (sufficient granular concept, necessary granular concept, sufficient and necessary granular concept) - Methods:
- fuzzy progressive learning for dynamic data updating
- two-way concept learning within multi-source formal context
- dynamic updating mechanism for three-way concepts
- granular concept-cognitive computing,
concurrent CCL - semi-supervised CCL
- dynamic CCL:
- fuzzy granular CCL
- memory-based CCL
- incremental CCL
- incremental concept tree
- progressive CCL
Methodologies
Cognitive Computing
- a computer system that simulates the cognitive process of human brain
- basic research focus:
- cognitive concept mechanism
- cognitive system construction
- simulated cognitive agent behavior
- decision analysis
- specific cognitive mechanisms for CCL:
- incremental learning
- fuzzy mechanism
- memory mechanism
- two-way learning mechanism
- multi-level cognitive mechanism
- four cognitive views for understanding concepts in cognitive psychology:
- classical view
- prototype view
- exemplar view
- theory-based view
Granular Computing (GrC)
FCA theory
fuzzy set theory
rought set theory
three-way decision theory
interval set theory
Fuzzy-based CCL: combine fuzzy set theory with CCL in a fuzzy formal context
- Advantages:
- Continuous data can be processed directly, without information loss during the discretization process.
- Fuzzy-based CCL can effectively handle the situation where the connotation of concepts cannot be accurately described.
- Methods:
- two-way CCL from a fuzzy-based progressive learning perspective and a multi-source information context
- CCL based on (weighted) fuzzy concept for concept classification
- fuzzy three-way concepts grounded in different information granularities for concept prediction
(Advantage over regular fuzzy concepts: knowledge depiction and cognitive bias reduction) - three-way concept analysis for concept description
- incremental learning of three-way concept
- three-way concept learning based on information fusion
- fuzzy granular CCL by three-way decision
- cognitive learning of approximate concepts
- interval-value CCL
- Advantages:
Machine Learning
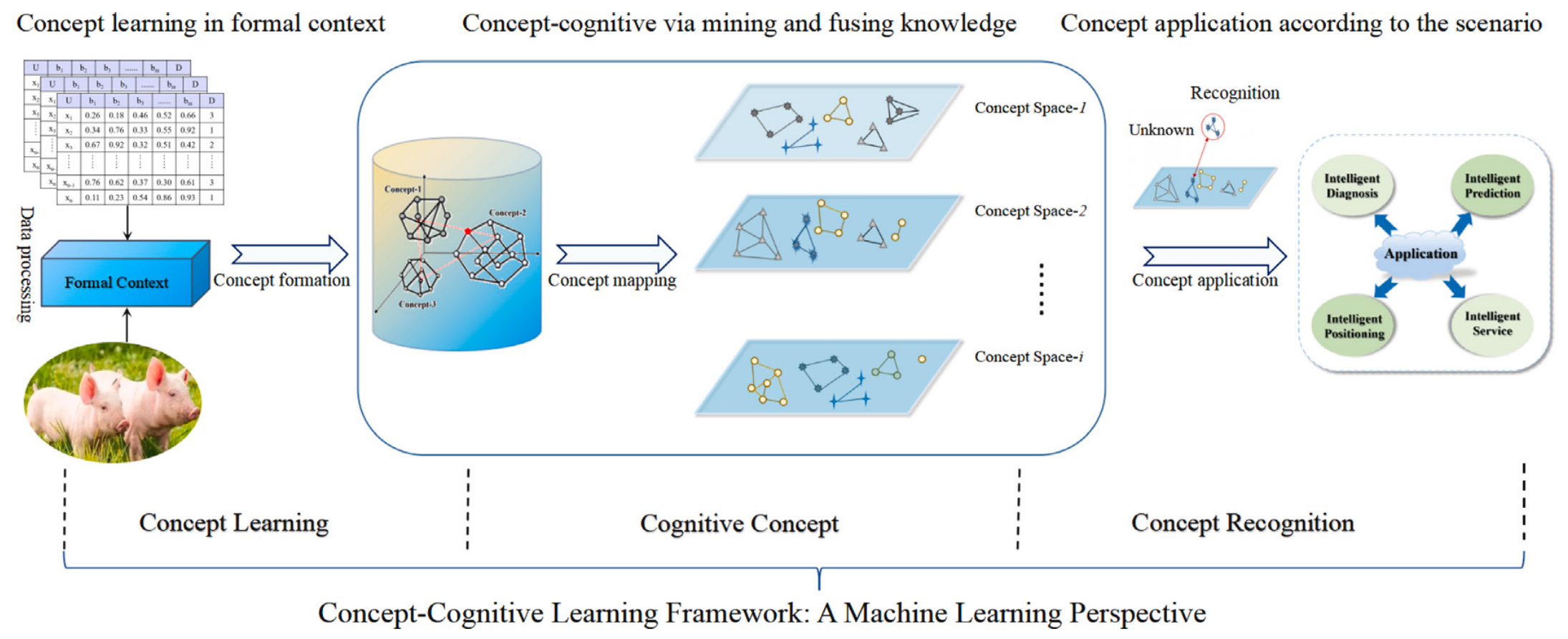
- Two tasks: concept classification, concept prediction
- Three stages:
- Concept learning:
- data processing for the formal context
- learning concepts in the formal context
- Concept cognition:
- concept formation via a pair of CCL operators
- mapping these concepts to different concept subspaces
- Concept recognition:
- concept recognition and knowledge discovery from unknown data
- Concept learning:
Challenges and Future Research
Concept Learning Method
- limited amount of available data (zero-/few-shot learning)
- dynamic data environment (RL)
Concept Cognition Mechanism
- incomplete data
- mixed data
- heterogeneous data
- multi-modal data
Cognitive System Construction and Optimization
- missing data
- fuzzy data
- insufficient cognition
- cognitive dimension uncertainty
- (integrating language understanding of concepts with other modalities)
- (developing effective cognitive learning operators)
- (evaluating effectiveness and stability)
Complex Decision Making
- discovering valuable information and knowledge from data to support human intelligent decision-making
- openness of decision environment
- virtualization of devision resources
- unstructured decision problems
- collaborative problem-solving
- multimodality
- spatio-temporal dynamics
- multi-source heterogeneity
Interdisciplinary Research
- deep CCL
- “large concept models”
- multimodal CCL
- spatio-temporal CCL
- (theories of concept representation and learning)
Engineering Applications
- real-world, industrial applications
- Title: Concept-Cognitive Learning Survey: Mining and Fusing Knowledge From Data
- Author: Der Steppenwolf
- Created at : 2025-04-22 16:47:56
- Updated at : 2025-06-22 20:46:50
- Link: https://st143575.github.io/steppenwolf.github.io/2025/04/22/Concept-Cognitive-Learning-Survey-Mining-and-Fusing-Knowledge-From-Data/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.