Qwen-VL: A Versatile Vision-Language Model for Understanding, Localization, Text Reading, and Beyond
Bai, Jinze, Shuai Bai, Shusheng Yang, Shijie Wang, Sinan Tan, Peng Wang, Junyang Lin, Chang Zhou, and Jingren Zhou. “Qwen-VL: A Versatile Vision-Language Model for Understanding, Localization.” Text Reading, and Beyond 2 (2023).
Motivation
- Current open-source Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) suffer from inadequate training and optimization, lagging far behind the proprietary models.
- The majority of open-source LVLMs perceive the image in a coarse-grained manner and lack fine-grained visual understanding ability.
Main Contribution
Qwen-VL series, a set of large-scale multilingual multi-task LVLMs based on Qwen-7B LM
- Qwen-VL: pre-trained checkpoint
- Qwen-VL-Chat: instruction-tuned checkpoint
- a visual receptor including
- a language-aligned visual encoder
- a position-aware adapter
- an input-output interface
- a 3-stage training pipeline
- a multilingual (English, Chinese) multimodal (text, image) corpus
Model Architecture
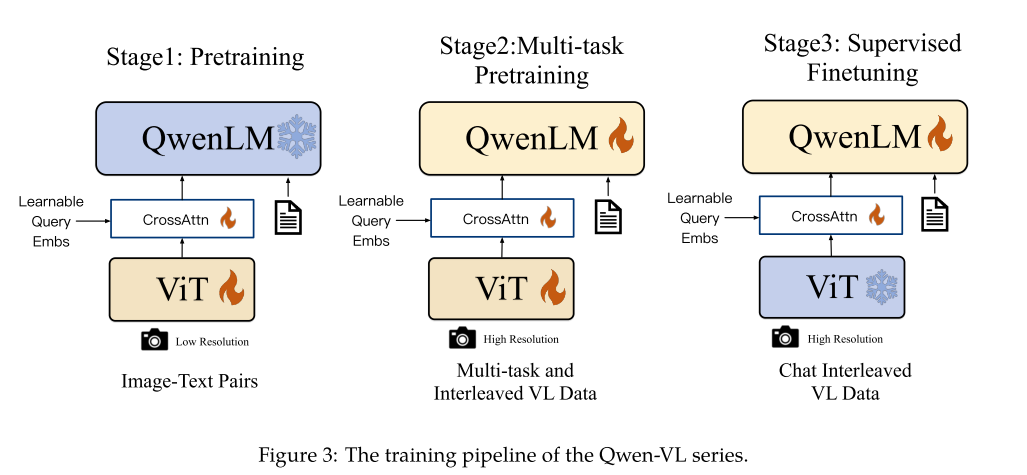
Large Language Model
- Architecture: Transformer, LLaMA
- Model: Qwen-7B (pretrained checkpoint)
- Model serves as text encoder.
Visual Encoder
- Architecture: Vision Transformer (ViT)
- Model: ViT-bigG
- Input: a set of resized images
- Model splits input images into patches with a stride of 14.
- Output: a set of image features
Position-Aware Vision-Language Adapter
- Motivation:
- efficiency issues caused by long image feature sequences
compression - potential loss of positional details during compression
positional encoding
- efficiency issues caused by long image feature sequences
- Architecture: a randomly initialized single-layer cross-attention module
- Funtionality: compress image features
- Cross-attention operation:
- queries: trainable embeddings
- keys: image features from the visual encoder
- compresses the visual feature sequence to a fixed length of 256
- 2D absolute positional encodings are incorporated into the query-key pairs.
- Input: query embeddings + image features from the visual encoder
- Output: compressed image features of length 256
- The output is then fed into the text encoder.
Input and Output
Image Input
- Relevant model components: visual encoder, VL adapter
- special tokens:
, - to differentiate between image feature input and text feature input
Bounding Box Input and Output
- Relevant model components: visual encoder, text encoder
- Bounding box are normalized to the range of [0, 1000) and transformed into a specific string format:
- This string is tokenized as text and does not require an additional positional vocabulary.
- Special tokens:
, : added to the beginning and end of the bounding box string, respectively - to distinguish between bounding box strings and regular text strings
, : added to the text strings which are referred to by the bounding box - to associate bounding boxes with their corresponding descriptive texts
Main Features of Qwen-VL Series
Support:
- multiple image inputs
- multilingual conversation
- multi-round dialogue
- text-reading (OCR)
- localization
- fine-grained visual recognition and understanding
Training
Pre-training
Pre-training data: image-text pairs
- large-scale
- weakly labeled
- web-crawled
- public available data + in-house data
- cleaned
original dataset size: 5B
cleaned dataset size: 1.4B (77.3% English text data, 22.7% Chinese text data)
Freeze text encoder, only optimize vision encoder and VL adapter.
Resize input images to
. Training objective: minimize cross-entropy of text tokens
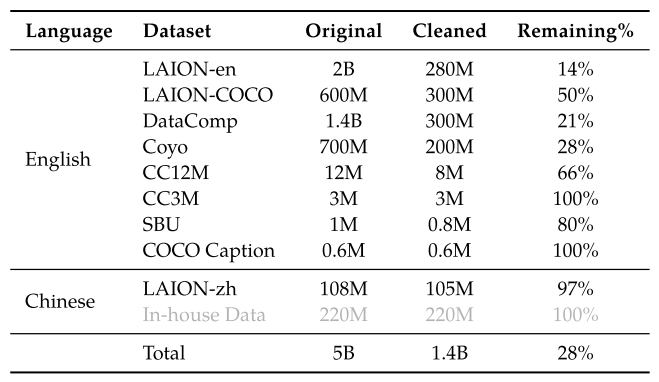
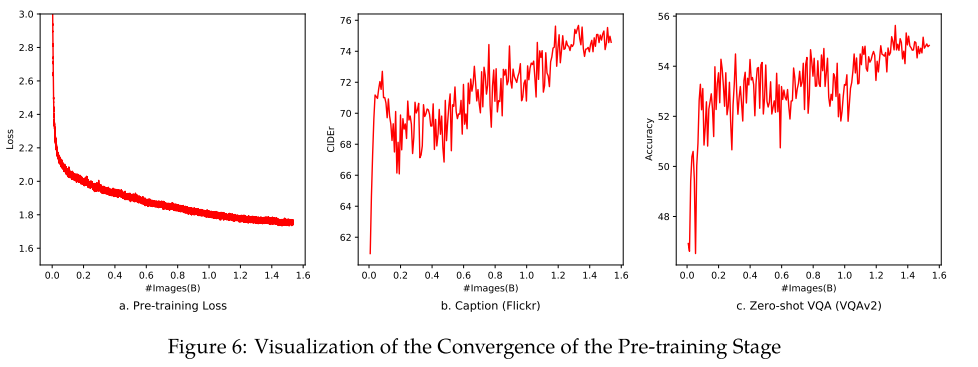
Multi-task Pre-training
Training data: interleaved image-text pairs
- high-quality with fine-grained VL annotation
- larger input resolution:
Ablate the window attention and global attention.
Jointly optimize the text encoder, visual encoder, and VL adapter.
Training objective: minimize cross-entropy of text tokens
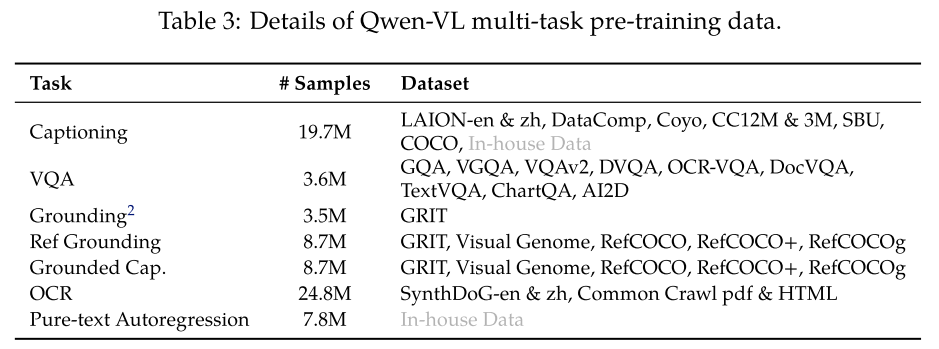
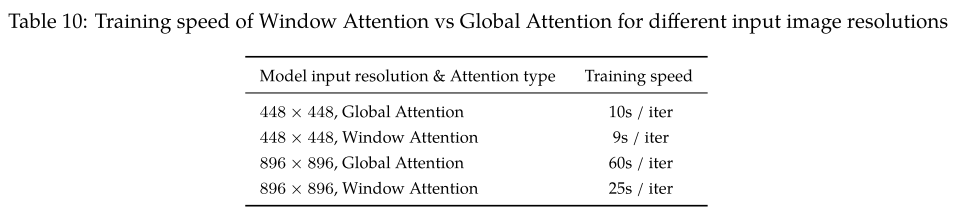
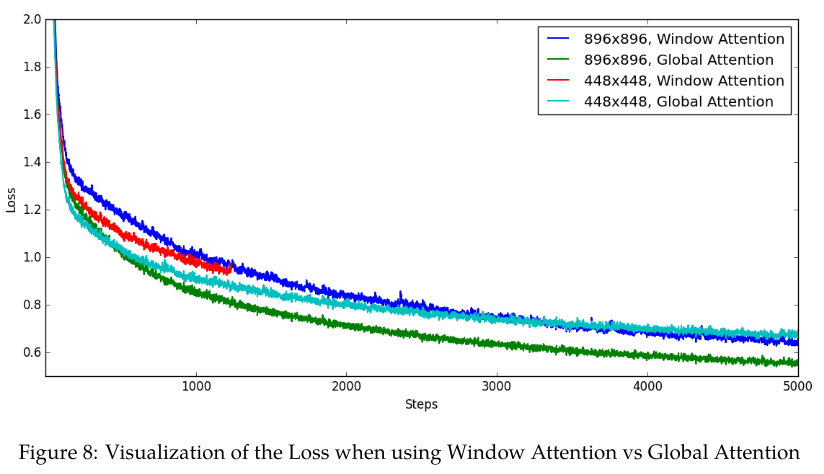
Supervised Fine-tuning (SFT)
Fine-tuning data:
- multi-modal instructions
- curated from cpation data and dialogue data
- generated through LLM self-instruction
- only address single-image dialogue and reasoning
- limited to image content comprehension
- additional dialogue data
- manual annotation + model generation + strategic concatenation
- incorporate localization and multi-image comprehension abilities
- Data size: 350K
- multi-modal instructions
Freeze visual encoder, optimize text encoder and VL adapter.
Evaluation
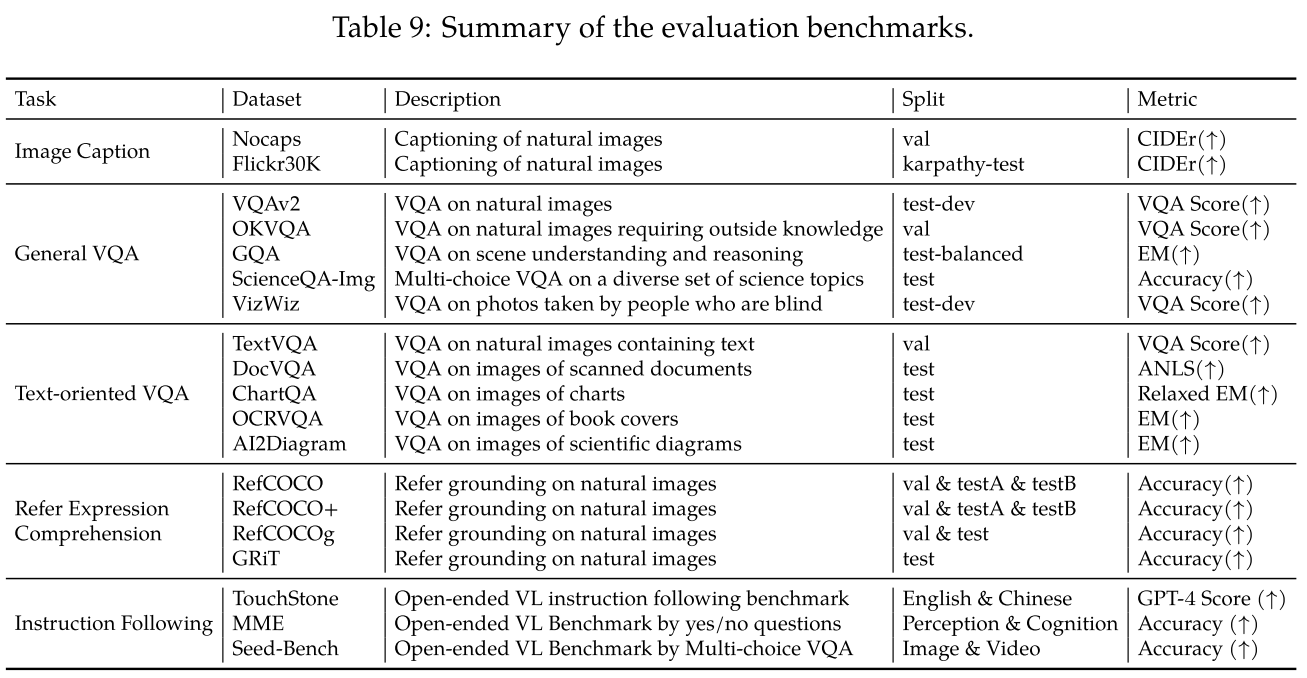
Image Caption and General Visual Question Answering
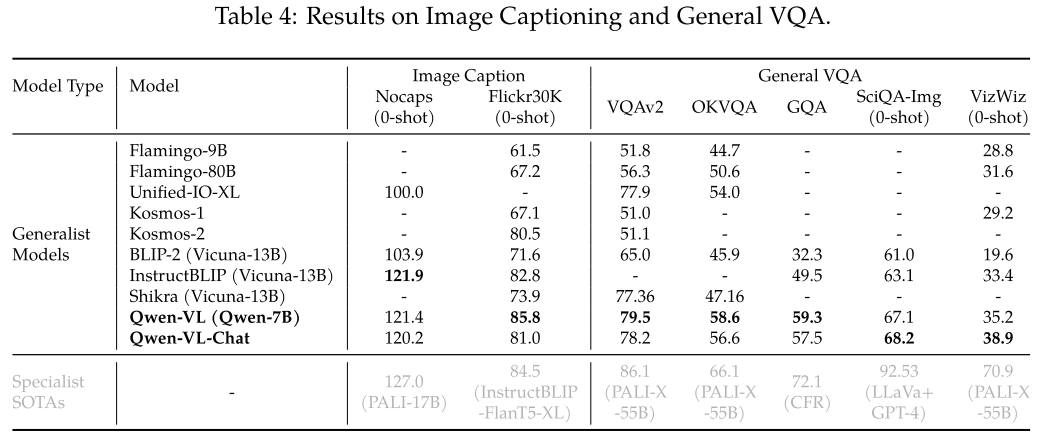
Text-Oriented Visual Question Answering
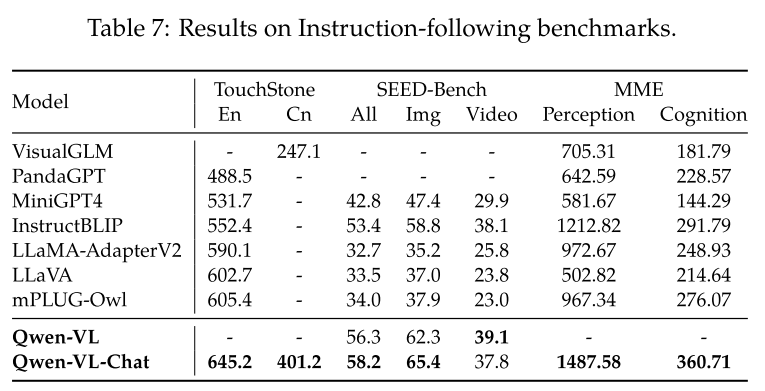
Refer Expression Comprehension
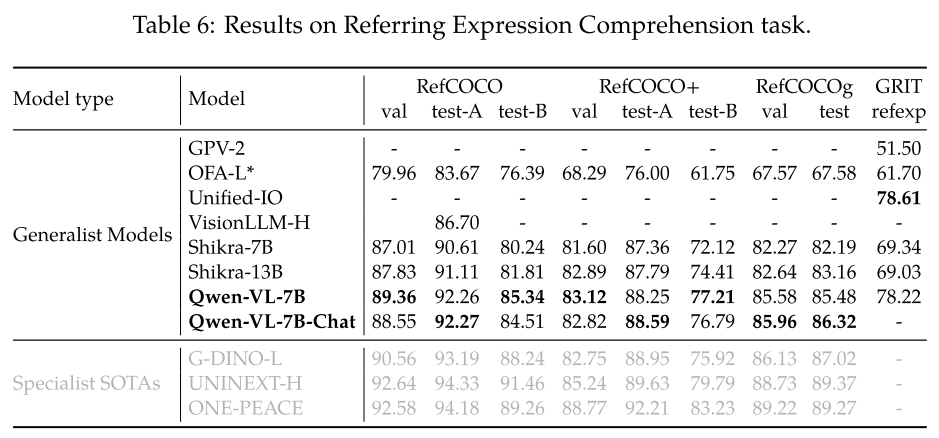
Few-Shot Learning on Vision-Language Tasks
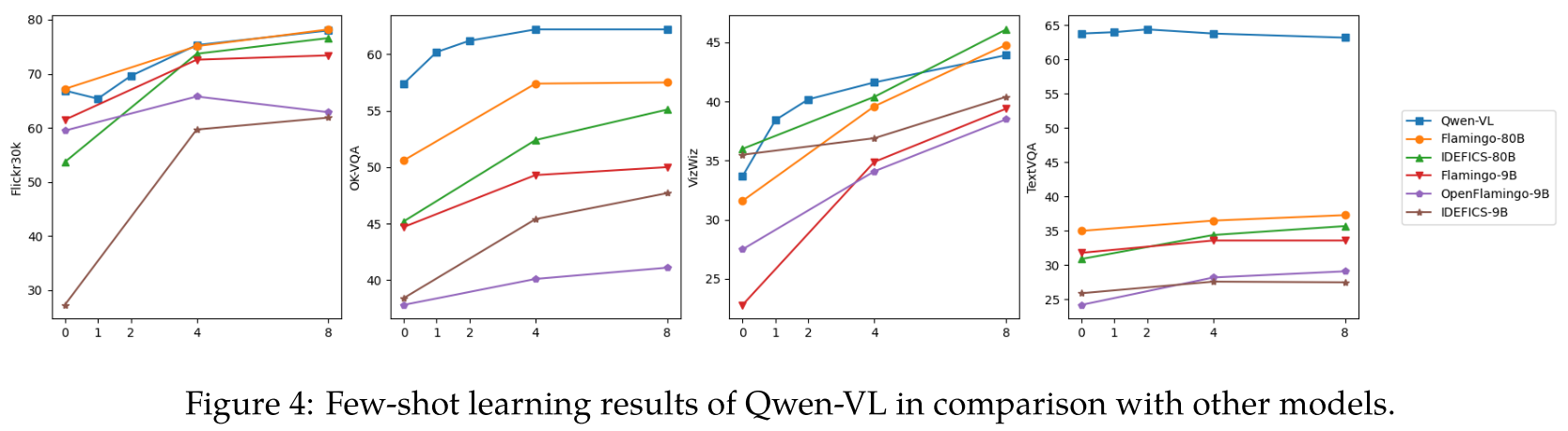
Instruction Following in Real-World User Behavior
- Title: Qwen-VL: A Versatile Vision-Language Model for Understanding, Localization, Text Reading, and Beyond
- Author: Der Steppenwolf
- Created at : 2025-02-25 23:49:12
- Updated at : 2025-06-22 20:46:50
- Link: https://st143575.github.io/steppenwolf.github.io/2025/02/25/Qwen-VL/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.