SmartBook: AI-Assisted Situation Report Generation for Intelligence Analysts
Reddy, R. G., Lee, D., Fung, Y. R., Nguyen, K. D., Zeng, Q., Li, M., … & Ji, H. (2023). SmartBook: AI-Assisted Situation Report Generation for Intelligence Analysts. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.14337.
What problems does this paper address?
Generating structured situation report from large volumes of news data by automatically discovering event-related strategic questions and multiple hypotheses (claims).
What is the motivation of this paper?
- Limitations of manually crafted situation reports:
- time-comsuming
- factual errors
- cognitive biases in the intelligence cycle
- sheer volumes of information makes deep analysis and critical thinking challenging
- excessively dense or incomprehensive information in the intelligence report
- Limitations of existing summarization approaches:
- generate plain text, without details, structures and high-level strategic information
- LLMs may return no answers or incorrect answers due to outdated information and lack of fact-checking
What are the main contributions of this paper?
- A comprehensive formative study and collaborative design process.
- SmartBook, an automated framework that generates comprehensive, up-to-date situation reports from disparate sources and presents them in an intuitive and user-friendly manner.
- A thorough utility evaluation involving intelligence analysts and decision-makers, investigating the usability of SmartBook.
- A content review to grade the quality of the generated report, and an editing study to understand the viability of SmartBook for producing preliminary drafts of situation reports.
What hypotheses does this paper make?
Automatic situation report generation can bridge the gap between reading and writing intelligence information.
What is the design strategy of SmartBook?
- Phase 1: Design and develop backend workflow, a frontend interface and multiple evaluation stages.
- Phase 2: Formative and collaborative design studies.
- Formative study: Learn the general needs and expectations from intel analysts for AI-driven systems.
- Technology is a means to enhance human capability that improves:
- research efficiency
- idea generation
- clarity of information
- AI is trustworthy and reliable as with humans since it provides:
- dependable information
- transparency in reasoning
- a foundation in verifiable facts
- Perspectives on roles of human intelligence analysts in training and guiding AI:
- 4 out of 10 analysts: advocate for substantial control over AI
- 6 out of 10 analysts: perceive AI involvement as an extension of routine oversight, akin to reviewing a junior colleague’s work
- Collaborative design: Gain an operational understanding of intel analysis process and generating situation reports, i.e. how to navigate, research and author situation reports.
- Three main themes:
- enhance analytical efficiency
- enhance transparency in AI systems
- enhance customization flexibility
- Four design strategies (DSs):
- DS1: reduce cognitive load, enhance analytical efficiency, user interface
- DS2: increase efficiency, automate time-intensive tasks
- DS3: trust and reliability
- DS4: customization and flexibility
- Three main themes:
- Technology is a means to enhance human capability that improves:
- Formative study: Learn the general needs and expectations from intel analysts for AI-driven systems.
SmartBook System Architecture
SmartBook = frontend user interface + backend framework
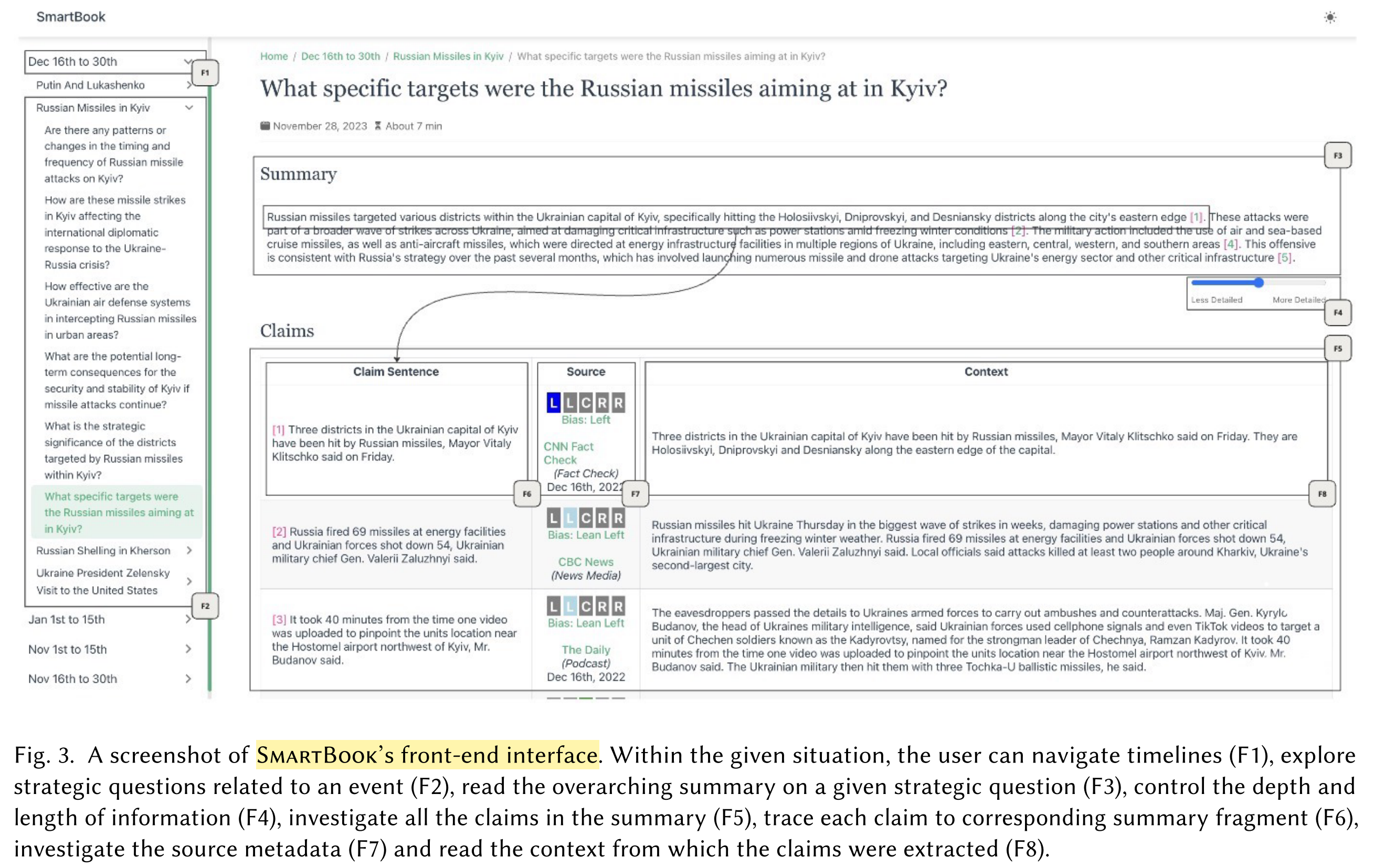
Frontend User Interface:
Backend Framework:
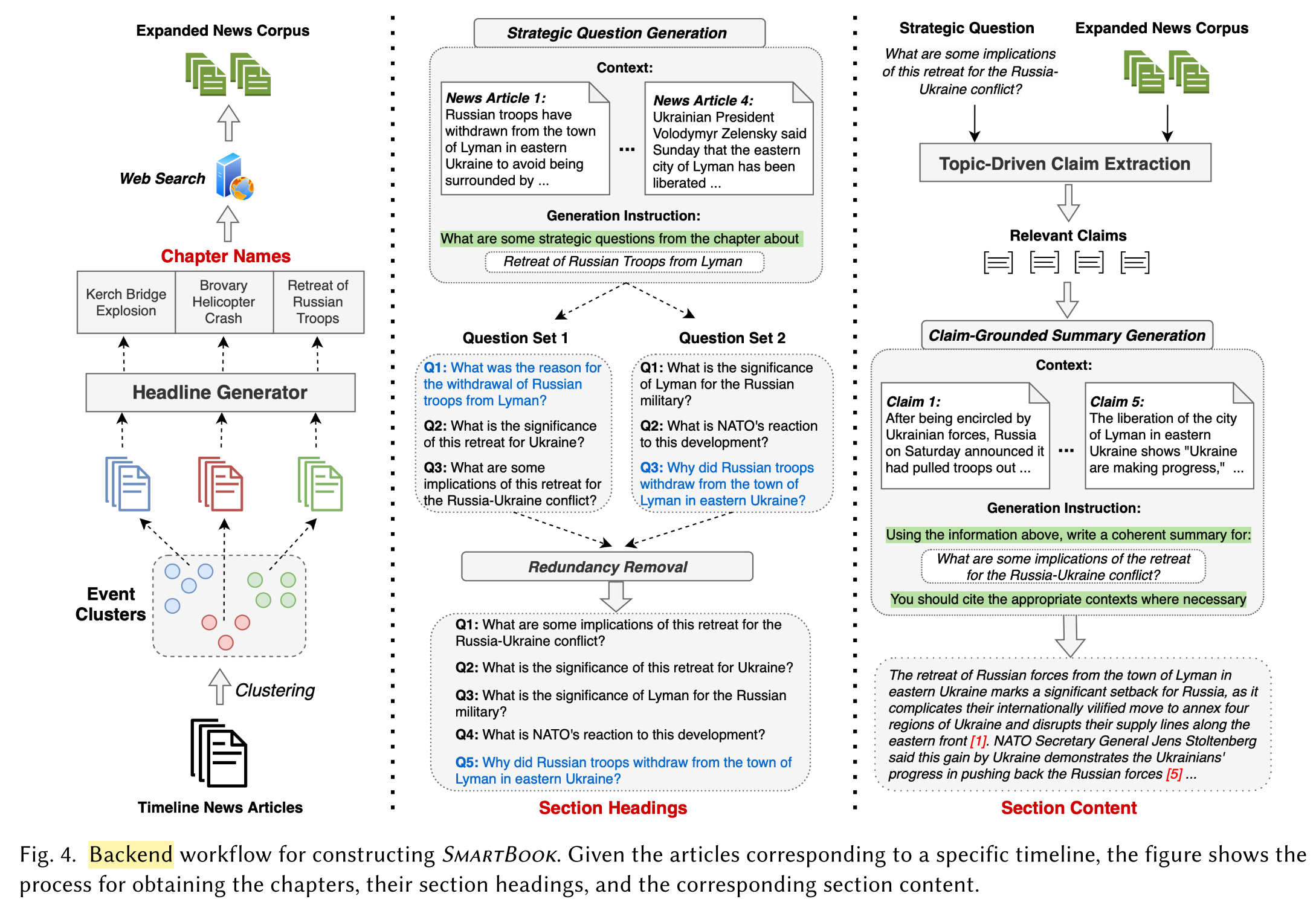
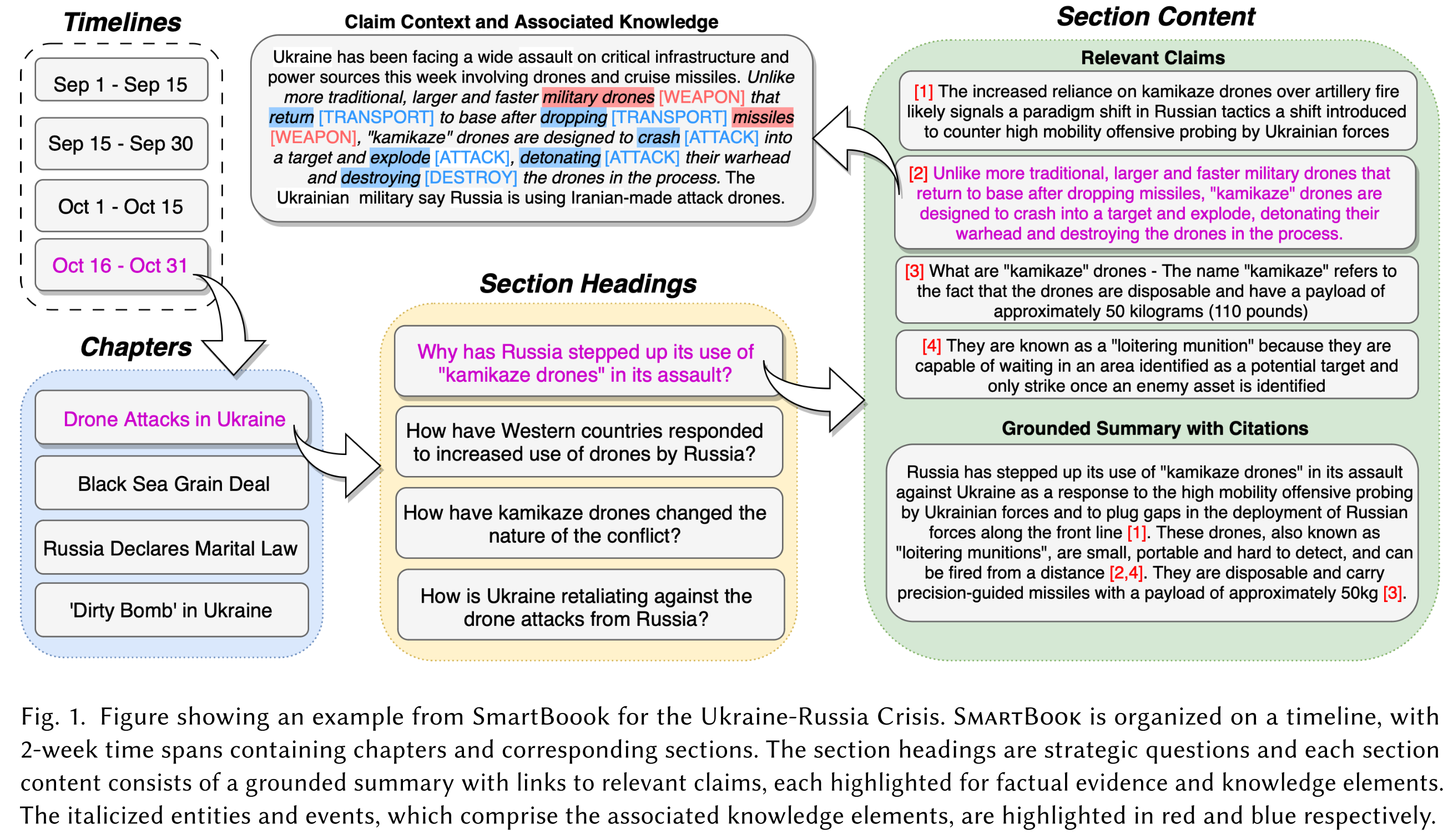
Major Events within Timespans as Chatpers.
- Insight: Situation reports cover event progressions over long periods. ==> It is beneficial to organize reports in the form of timelines, enabling seamless report updates with new events and helps facilitate users tracking and understanding of situation context.
- Identify major events:
- Method: Cluster daily news summaries into major event groups (agglomerative hierarchical clustering based on TF-IDF)
- Input: news summaries
- Output: clusters of news snippets
- Improve the comprehensiveness of each event cluster by expanding the news corpus:
- Method: Generate a headline for each event cluster as chapter name:
- Model: NHNet, a BART-based news headline generation model trained on NewsHead dataset
- Input: concatenated title and text from all the news snippets within the an event cluster
- Output: a short event heading (chapter name, aka. topic)
- Use the chapter name as query to retrieve additional relevant news articles via Google News.
- Method: Generate a headline for each event cluster as chapter name:
Strategic Questions as Section Headings.
- Insight: A situation report should have a logical structure and descriptive section titles for clarity and easy access to information for intelligence analysts.
- Generate strategic questions relating to each major event as section headings:
- Questions cover insights such as:
- motivations behind actions in an event, and
- its potential future consequences
- Model: GPT-4
- Input: context (news articles from an event cluster) + generation instruction
Generation instruction:
“What are some strategic questions from the chapter about <chapter name>“
- Output: sets of strategic questions, each related to a major event
- Questions cover insights such as:
- De-duplicate repeated questions across different question sets:
- Model: RoBERTa-large
- Input: sets of strategic questions with duplicates
- Output: a set of unique strategic questions
Extraction of Claims and Hypotheses.
- Insight: Intelligence analysts need systems that quickly identify key information in documents.
- Model: a QA pipeline based on RoBERTa-large (https://aclanthology.org/2022.coling-1.603/)
- Input: news snippets + strategic question
- Output: answer extractions (extracted claim == sentence containing the answer)
- Issue: high-confidence false positives ==> validation of answers
- Verify each context against the strategic question.
- Model: an answer sentence selection model (https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/6282)
- Input: an extracted claim
- Output: a validation score ranging from 0 (incorrect) to 1 (correct)
- Select the top-5 relevant contexts for summarization.
Grounded Summaries as Section Content.
- Issue: LLMs suffer from hallucinations in generation.
- Insight: Factuality is far more important than creativity for situation report generation.
- Detail levels of summary: brief (2-3 sentences), standard (4-6 sentences), extended (2 paragraphs)
- Model: GPT-4
- Input: top-5 most relevant contexts (claim sentences) + instruction
Instruction:
“Using the information above, write a coherent summary for:\n What are some implications of the <topic>\n You should cite the appropriate contexts where necessary.”
- Output: a concise summary
How is the generated report presented to the user?
Utility Study: Evaluation of the System
Conduct an interview with semi-structured questions and a post-study questionnaire on the usability of SmartBook.
Each user study session has four parts:
- an introductory overview
- a free-form investigation
- a guided exploration
- a concluding reflective discussion
Participants: 10 intelligence analysts, 2 decision-makers from Canadian government boards
Research Questions:
- RQ1: How do intelligence analysts interact and leverage the features within SmartBook?
- RQ2: Do intelligence analysts find SmartBook intuitive, usable, trustable and useful?
- RQ3: How do decision-makers interact, perceive and use SmartBook?
How was the utility study conducted?
- Participants receive a concise introduction to the SmartBook system.
- Participants freely investigate the system, exploring at least three questions across five chapters of their choice.
- Participants are systematically introduced to the system.
- Conduct a semi-structured interview to gather reflective feedback on the system’s efficacy and potential areas of enhancement.
- Participants fill out a post-study questionnaire.
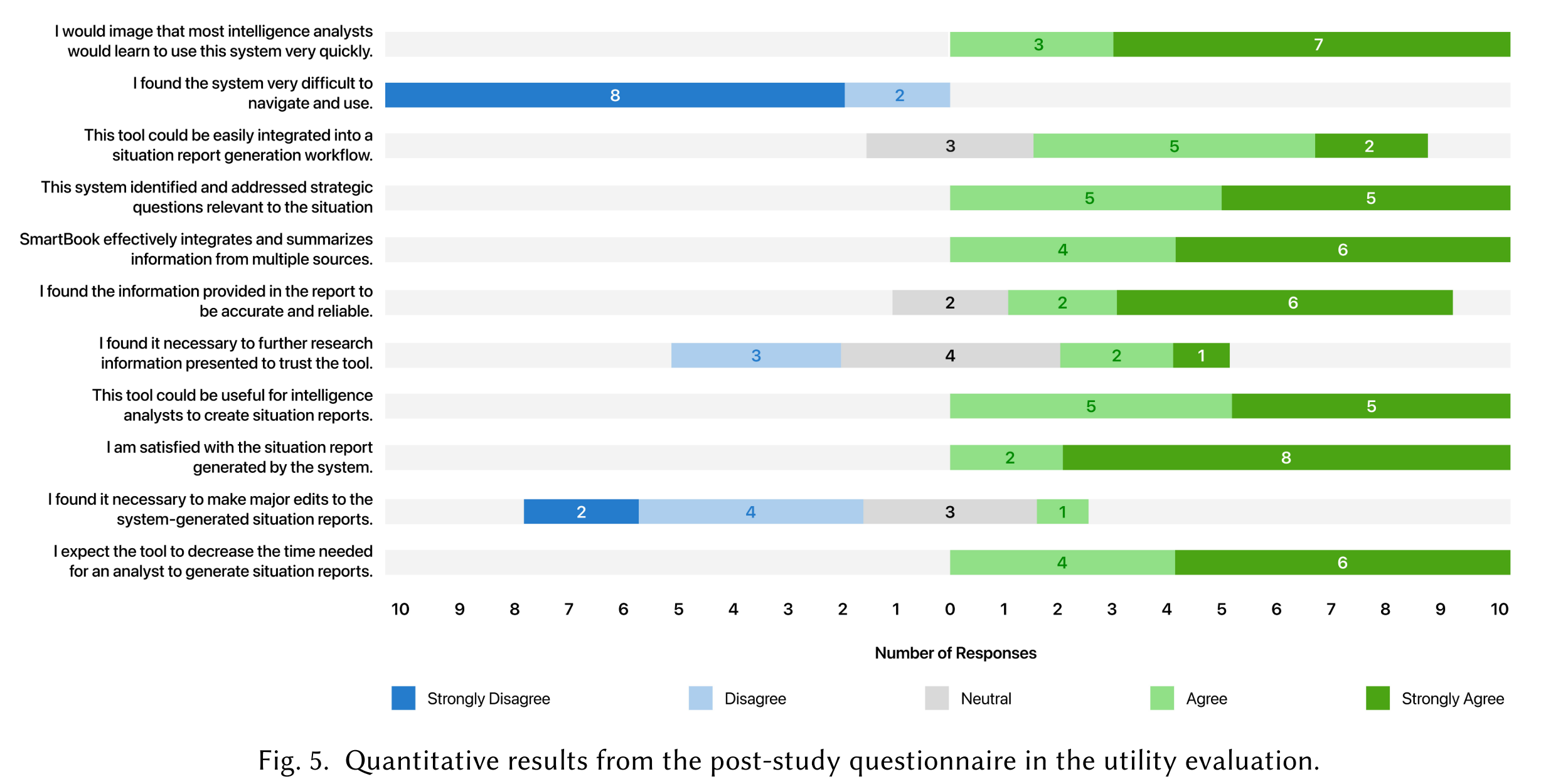
What questions are asked in the post-study questionnaire? What are the responses of the participants?
- I would images that most intelligence analysts would learn to use this system very quickly.
- I found the system very difficult to navigate and use.
- This tool could be easily integrated into a situation report generation workflow.
- This system identified and addressed strategic questions relevant to the situation.
- SmartBook effectively integrates and summarizes information from multiple sources.
- I found the information provided in the report to be accurate and reliable.
- I found it necessary to further research information presented to trust the tool.
- This tool could be useful for intelligence analysts to create situation reports.
- I am satisfied with the situation report generated by the system.
- I found it necessary to make major edits to the system-generated situation reports.
- I expect the tool to decrease the time needed for an analyst to generate situation reports.

UI Understandability and Interaction: positive answer to RQ1
Building Trust on SmartBook: positive answer to RQ2
Perceived Benefits for Intelligence Analysts: positive answer to RQ2
SmartBook as a Learning Tool for Decision-Makers: positive answer to RQ3
Content Review: Evaluation of the Generated Content
Evaluation of Strategic Questions
- Strategic Importance
- Amount of Tactical Information
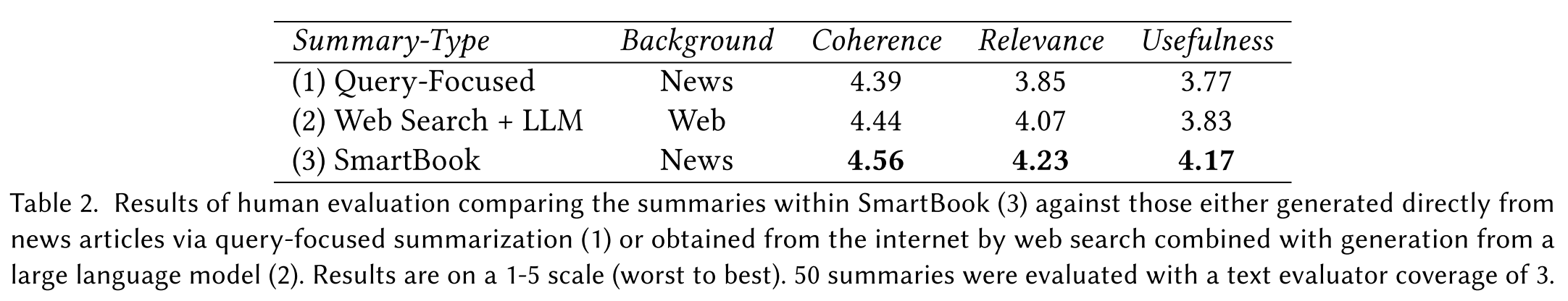
Evaluation of SmartBook Summaries

- Baselines:
- query-focused summarization
- Given a strategic question as query, process entire news articles directly with an LLM to generate summaries.
- web search + LLM
- Use relevant web pages from the internet serve as input context to the LLM for summarization.
- query-focused summarization
- Evaluation Metrics: scores ranging from 1 (worst) to 5 (best)
- coherence
- relevance
- usefulness
Evaluation of Citation Quality
Evaluation Metrics:
- citation precision
- citation recall
Metrics are calculated using the TRUE model.
Result: citation precision 64.7%, citation recall 69.2%
Editing Study: Evaluation as a Preliminary Draft

An expert analyst actively explores SmartBook’s features and then edits 94 randomly selected summaries from generated situation reports, until they meet professional intelligence reporting standards.
Evaluation Metrics:
- BLEU (token-level)
- ROUGE (token-level)
- Levenshtein edit distance (character-level)
Results and Conclusions:
Result: BLEU: 59.0%, ROUGE-L: 74.1% (high token overlap between the generated and post-edited texts)
Conclusion: SmartBood-generated reports have sufficiently high quality, such that extensive human expert revision may not be necessary.Result: Levenshtein distance: 34.4%
Conclusion: There still exists a gap between generated summaries and human expert curation.Result: The analyst predominantly added rather than removed content.
Conclusion: Automated summary generation may generally lack details.Results: 15% of the generated summaries did not need any human modifications.
Conclusion: SmartBook is proficient in creating acceptable reports in some scenarios without human intervention.Overall conclusion: SmartBook provides a good starting point for analysts to expand upon for the generation of situation reports.
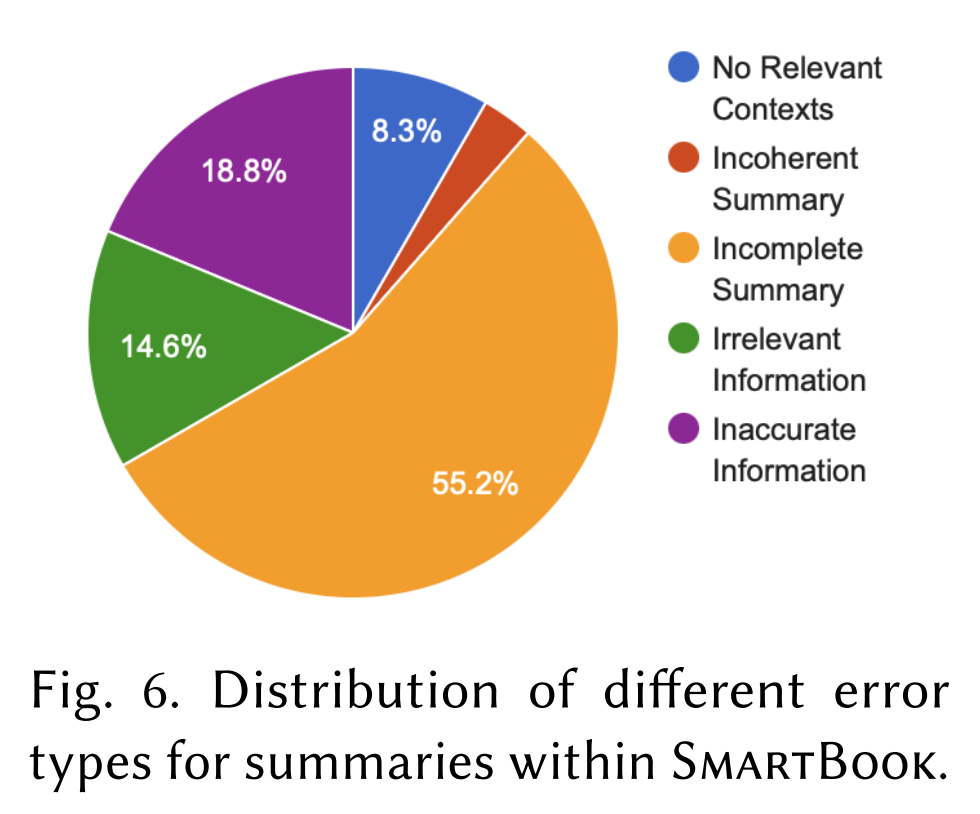
Ask the expert analyst to categorize the errors in the generated summaries:
- No relevant contexts: None of the extracted contexts are relevant to the strategic question.
- Inaccurate information in summary: Summary contains incorrect information that does not reflect the underlying input contexts.
- Incoherent summary: Summary is incomprehensible and unclear.
- Incomplete summary: Important information in the input contexts is missing in the summary.
- Irrelevant information in summary: Summary has meterial that is not relevant to the question, despite some relevant extracted contexts.
How does SmartBook differ from previous systems?
- factural accuracy
- analytical depth
- efficiency in structured, data-driven tasks
- less creative and more rigorous
What are the main advantages and limitations of this paper?
Advantages:
- The proposed SmartBook system effectively identifies critical strategic questions, ensuring that downstream readers receive targeted, relevant, and evidence-grounded information to aid decision-making processes.
- The system provides human intelligence analysts with a valuable preliminary draft of a situation report.
- The citations enhance the trustworthiness of the summaries by allowing verification against the cited sources.
Limitations:
- unverified news source credibility
- potential inaccuracies in reflecting source material despite citations
- user studies mainly focused on military intelligence analysts, which may not represent the needs of a wider analytical audience
- Events in news articles are simply clustered, but not extracted. It remains unclear whether it would be beneficial to first extract structured events.
What are potential future extensions?
- Incorporating multimodal, multilingual information.
- Controlling the bias of news sources.
- Co-authoring with iterative refinement.
- Improving reliability of the genrated reports.
- Title: SmartBook: AI-Assisted Situation Report Generation for Intelligence Analysts
- Author: Der Steppenwolf
- Created at : 2024-12-09 21:55:32
- Updated at : 2025-06-22 20:46:51
- Link: https://st143575.github.io/steppenwolf.github.io/2024/12/09/SmartBook/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.